Developing and adding models to NoM
The NoM Client can be used to run local models by including a local_server configuration to the NoM configuration file. This local_server configuration entry can be in addition to the configurations you may have pointing to external NoM Server instances.
Note: Running models using the local_server configuration does not require the use or connection to any other NoM server.
conf = {
"servers": {
"local_server": {
"type": "local_server",
"models_directory": "<PATH TO NOM MODELS DIRECTORY>",
"working_directory": "<PATH TO WORKING DIRECTORY>"
}
"ext_dev_rest_server": {
"type": "rest",
"server_addr": "https://nom-dev.esa.int",
"api_version": "api",
"api_key": "<API KEY>"
}
}
}
NoM Models directory
The NoM models directory can be placed anywhere accessible on the filesystem.
This directory contains sub-directories containing the individual model packages.
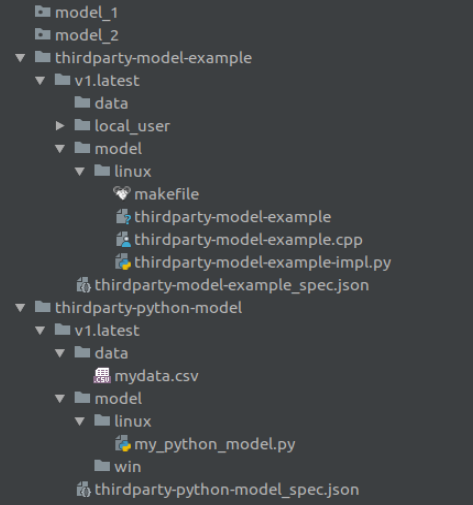
Within each model package directory, one or more versions of the model can be placed. The latest version should be post-fixed with '.latest'.
Within each version directory, there needs to be:
- model specification
- model directory containing the platform specific model code
- optional data directory
Within the model directory, subdirectories referring to the particular platforms need to be present. Not all platforms need to be present. THe following platforms are supported.
- linux
- win
- macos
An example, third-party C++ model can be found here.
An example, third-party python model can be found here.
Models that run within the NoM framework consist of either a model binary file, or a python model script. In addition to the runnable code, a python module for the model implementation needs to be supplied. This model implementation file should implement the ModelImplementation interface.
Optionally, a python module for the results processing can be supplied, implementing the OutputReader interface as defined by ...
Creating a model specification
{
"meta": {
"version": "v1",
"model_name": "thirdparty-model-example",
...
},
"system": {
...
"location": "{{CONFIG::NOM_MODEL_BINARY_DIR}}",
"binary": "thirdparty-model-example",
"model_provider_class": "ThirdpartyModelImplementation",
"model_provider_location": "{{CONFIG::NOM_MODEL_BINARY_DIR}}/thirdparty-model-example-impl.py"
},
"inputs": [
...
],
"outputs": [
...
]
}
Running the model
When the model is run through the NoM Client, the model inputs along with other context data is made available to the model implementation code.
class ModelImplementation:
"""
Model implementation base class.
"""
def run(self, **kwargs):
model_inputs = None
if "run_context" in kwargs:
run_context = kwargs["run_context"]
model_inputs = run_context.model_inputs
else:
run_context = None
if "working_directory" in kwargs:
working_directory = kwargs["working_directory"]
else:
working_directory = None
model_inputs = run_context.model_inputs
# Get the results from the model input group named 'mymodel' (as defined in the model specification)
model_inputs = model_inputs["mymodel"]
# Create a unique name for use in any output files
run_context.run_tag = run_context.username + '_' + run_context.project_name + '_' + run_context.tag
...
# run the model
...
Returning the results from a model
For each result defined within the outputs section of the model specification, a ModelResult needs to be created. Using a formatted results dictionary (below), the OutputReader.create_results can be used to create the the ModelResult for each.
{
"model-name": {
"data": {
"column1": [...],
"column2": [...],
"columnN": [...]
},
"meta": ...
}
}
model_results = OutputReader.create_results(results_in=return_data, run_context=run_context)
msr = ModelRun(run_context=run_context,
model_results=model_results,
status="siccess",
status_code=0,
message="Model run successful")
return msr
Note: if the model has failed you can return a failed model run:
msr = ModelRun(run_context=run_context,
status="failed",
status_code=-1,
message="Model failed .. reason")
return msr
Access to this repository can be requested by emailing space-env@esa.int
